MacVector 18.7
(released July 2024)
Overview
MacVector 18.7 introduces a History tab to track the construction of your expression vectors and clones. It also includes new features for codon optimization, such as direct support for Codon Usage Tables (CUT/.bias) and the ability to create custom Codon Usage Tables files from your sequences. Additionally, MacVector 18.7 enhances Assembler’s toolkit by adding a new reference assembler for mapping PacBio and ONT sequencing reads to your reference sequences.
MacVector 18.7 also makes it easier to store your own Restriction Enzyme files when multiple people use the same Mac (ideal for that shared lab Mac!).
..and as usual there are a lot of enhancements to existing features such as protein pI calculations.
MacVector 18.7 was developed on macOS Sonoma and is supported on macOS High Sierra to macOS Sonoma. It has also been tested on early development releases of macOS Sequoia and will be fully supported when Apple release it. MacVector 18.7 is a Universal Binary that will run on Apple Silicon Macs and Intel Macs.
Long-Read Reference Alignments using minimap2
The addition of Minimap2 allows Assembler to map noisy long-read data from Pacific Biosciences or Oxford Nanopore to a reference sequence(s). Minimap2 is similar to Bowtie2 but optimized for handling long reads instead of short reads under 500 nucleotides. Additionally, Minimap2 also excels at assembling short read data and may even out-perform Bowtie2 in certain situations.

Translate All CDS Features
You can now easily translate all CDS features in a sequence with the new menu option Analyze | Translate All CDS Features. This is useful for translating proteins in bacterial genomes or eukaryotic sequences. You can choose to display all translated proteins in fasta format or create a codon usage table from the results.
Translate All CDS Features in Folder
There is a new Database | Translate All CDS Features in Folder menu option that is similar to Translate All CDS Features except that it takes a source folder and then loads every sequence file in the folder and translates each CDS feature that it finds, accumulating the results and offering the same result options as Translate All CDS Features. A Codon Usage Table viewer window is always created and displayed when you select this option.
Codon Usage Table Viewer
MacVector now includes a viewer for codon usage tables (CUT/.bias) files. This displays the data in a standard text format with one row of data per codon, identical to codon usage output windows used in other MacVector translation functions.

You can import Codon Usage Tables from CUT files available on codon usage websites such as CUTG. You can also generate custom CUT files by using the new Translate All CDS Features from a single sequence or from multiple sequences using the new Translate All CDS Features in Folder tool. You can invoke this multiple times and slowly build up the codon usage information from a large sequence data set in multiple folders.
History Tab
There is a new tab in nucleic acid single sequence windows called History. This tab lists several MacVector-specific features relating to the editing history of the sequences such as ‘frag’ and ‘edit’. These features now contain additional information such as the date of the operation, the name of the user who performed it and additional sequence information. In the future, all MacVector sequence modifications will write out this information allowing the full history of any construct to be determined and even allowing a simple reversion of the construct to how it existed on a specific date

Change in Default Restriction Enzyme File Location
MacVector now saves restriction enzyme files in a new location (~/Library/Application Support/MacVector/Restriction Enzymes/) within a user’s home folder. This is always writeable, even without Administrator access. If you have already saved files in a different location, they will not be affected. MacVector will automatically populate the new directory with the latest restriction enzymes and update any user-edited files from the old location.
Miscellaneous Enhancements and Bug Fixes
- The Align to Reference SNPs tab now also displays the percentage of each residue present in each heterozygote SNP.
- The Align to Reference consensus calling threshold default has been raised to 70% so that heterozygous SNPs are more consistently reported on the consensus line.
- A crash when repeating heterozygote analysis has been fixed.
- Copied fasta text data is now more reproducibly parsed as single sequence data by New From Clipboard.
- The protein pI calculations have been modified to also report the pI ignoring Trp and Cys residues. This brings the results more in agreement with the popular ExPASY website.
- A bug where the “blocking” for protein sequences was taking the DNA values has been fixed.
- Exporting sequence data in the Sequin .tbl format now correctly writes out the correct sequence for the minus strand of segmented features.
MacVector 18.6
(released July 2023)
Overview
MacVector 18.6 contains a wide variety of new or enhanced functionality, adding features such as one-click optimization of CDS coding regions, automatic phrap sub-project assembly of ABI reads based on naming, direct support of .csv and .tsv text files for Primer Database searching, optional inclusion of graphical information in GenBank exported sequence files and numerous tweaks and improvements to many different workflows.
MacVector 18.6 was developed and tested on macOS Ventura. It is supported on macOS High Sierra to macOS Ventura. MacVector 18.6 has also been tested on the upcoming macOS release, macOS Sonoma and will be fully supported on it when Apple release it. MacVector 18.6 is a Universal Binary that will run natively on Apple Silicon Macs as well as existing Intel Macs.
Direct Codon Optimization of CDS Features
There is a new Analyze function that will directly optimize codon usage of CDS features for enhanced expression in a different organism. Simply select a CDS feature in the Map or Features tab of a nucleic acid sequence and choose Analyze | Optimize Codon Usage for CDS… The resulting dialog lets you choose the codon usage table (.bias file) to use, along with the genetic code and the optimization algorithm. A filter dialog after the algorithm runs lets you choose whether or not to apply the results to the original CDS, or to simply view the proposed changes.
When optimized a new Feature is annotated to the sequence showing that the CDS has been optimized, which algorithm was used and which codon usage table. It will also show the user who made the modification, date, and how the sequence was before and after the action.

Automatic Assembly of Sub-projects with Phrap
A new tab in the phrap parameters dialog lets you have MacVector automatically break out the input reads into sub-projects to be assembled separately. A simple pattern-matching text box lets you define which characters in the input filenames should be treated as project names, and which should be treated as read names. After assembly, contigs can be exported (to a variety of file formats, including fasta/fastq) retaining the project name in the contig names. A great time saver if you do a lot of related small sequencing projects using a well-defined naming convention.


Heterozygote Analysis Enhancements
There is a new checkbox to suppress the default normalization that the heterozygote analysis algorithm uses to better identify potential heterozygotes. Sometimes, clear heterozygotes may be missed if the combined peaks are significantly lower than would be expected in that area of the chromatogram. For example when a genome has multiple copies of a gene, but a SNP exists in only one of those copies. However, turning off normalization can result in an increase in false positives.
When performing a heterozygote analysis on assembled reads (Align to Reference or Contig Assembly) the output now includes the location of the potential SNP in the consensus/reference sequence.

Direct Support for .tsv and .csv Primer Database Files
The Analyze | Primer Database Search function (and the associated Scan DNA -> Primers feature) can now use appropriately formatted text .tsv or .csv files such as those that might be exported from Microsoft Excel, without having to import them into MacVector and save in the MacVector .nsub format. The data should have 4 columns — /// where and are optional. If the column is present, the values can only be “0” (unselected) or “1” (selected). The sequence should conform to the standard IUPAC code and “tails” on primers should be indicated by lower case. The use of a header row is optional.
Custom Genbank Export
There is now an option to export sequences in a GenBank text format that includes the graphical feature appearance information that is normally only available in MacVector .nucl files. GenBank is a simple text format, so you can view the resulting files in a text editor and it’s easy to modify the graphical information in those files if you need to. You can then import back into MacVector with those graphical changes fully intact. This new “enhanced” GenBank format can completely substitute for a standard MacVector .nucl file if you or your institution really requires a plain text format for submission to a database or other text-based repository.
Documenting the history of a vector.
- The MacVector-specific ‘frag’ features now include the name of the user who made the change.
- There is a new MacVector-specific ‘edit’ feature that describes edits made to a sequence with the date the change was made and the user who made the change. Currently, this is only created by the Optimize Codon Usage for CDS function, but eventually this will be the basis for a comprehensive history function throughout MacVector.

Miscellaneous Enhancements and Bug Fixes
- There have been some fixes to the Protein Toolbox Analysis code to help prevent certain very rare crashes.
- The Restriction Enzyme Picker has been updated to display the number of cuts for each enzyme.
- Invoking Select All in the Restriction Enzyme Picker now ONLY selects the VISIBLE enzymes in the picker. This makes it much easier to manipulate lists of interesting enzymes.
- There is a new context sensitive menu item in the Contig Editor and Align to Reference Editor that lets you manually change the “clipping” (also known as “trimming”) positions at the beginning and ends of sequences.
- There are enhancements in the Align to Reference scoring algorithm to more closely reflect parameters set by the user.
- There is a “mouse-over” tooltip in the Align to Reference and Contig Editors that displays more information about the read and the alignment score.
- The window size of each type of window is now remembered each time you close one, so that a subsequent window of the same type will open at that size.
- There is now a context menu item to control how read names are truncated in the Align to Reference and Contig Editors.
- You can now hold down [OPTION] + [SHIFT] to temporarily switch from the normal “Zoom To Sequence” mode in the Map tab to “Select Sequence”.
- Phrap parameters are now remembered between invocations like most other MacVector parameters.
MacVector 18.5
(released Sept 2022)
Overview
MacVector 18.5 was developed and tested on macOS Ventura. It is supported on macOS High Sierra to macOS Ventura and is a Universal Binary that will run natively on Apple Silicon Macs as well as existing Intel Macs.

Heterozygote Analysis of Sanger trace files
- The heterozygote analysis tool analyzes one or multiple Sanger trace files and reports on all possible heterozygotes.
- You can also analyze Sanger trace files and permanently change the basecalled sequence with an IUPAC ambiguity code representing the called heterozygote.
- The tool works on multiple trace files in the Assembly project manager or the Align to Reference editor.
- You can also basecall heterozygotes in a trace file in the Single Trace Editor.

Align to Reference supports long reads
Long sequencing reads from PacBio and ONT sequencers can now be assembled in Align to Reference.
Miscellaneous enhancements
- Importing Sequencher project (.SPF) files has been significantly enhanced.
- As usual there’s been a lot of bug fixes and changes that you probably do not care about! But be assured that everything we do makes MacVector a future proof and modern macOS application that you can rely on!
MacVector 18.2
Released November 2021
Overview
MacVector 18.2 is a Universal Binary that runs natively on both Apple Silicon and Intel Macs. It is supported on macOS Sierra (10.12) to macOS Monterey (12).

Align to Reference Enhancements
The Align to Reference alignment algorithm has been overhauled to do a much better job handling larger numbers of gaps in the alignment between a reference sequence and a read.
The alignment algorithm has been further optimized for speed. In addition, the Sensitivity setting can now be lower due to the enhanced consecutive gap detection, which also speeds up calculations.
When aligning ABI chromatogram data, or plain sequences, the Map tab now graphically displays the “trimmed” regions at either end of the sequences.
There is a new Remove Gaps context-sensitive (right-click) menu option that deletes residues in reads that correspond to a gap in the consensus sequence.
Context Sensitive Hamburger Menus
Where a window has a context-sensitive menus available these views now contain a “hamburger” button (three parallel horizontal lines) that displays the same context sensitive menu when clicked on.
Importing of Primer Databases in TSV or CSV Format
You can import primer data into a MacVector Primer Database (.nsub) file from an Excel or CSV formatted file. This functionality replaces the old Primer Converter utility.
Miscellaneous Enhancements
To reduce clutter in the Assembly Project window toolbar, all of the assembly algorithms have been consolidated into a single Assemble toolbar button with a dropdown menu.
MacVector 18.1
Released January 2021
Overview
MacVector 18.1 is a Universal Binary application that means it runs natively on Apple Silicon and Intel Macs.
Universal Binary
MacVector 18.1 is a Universal Binary, meaning that it can run natively on both Intel and Apple Silicon Macintosh computers. Other than the ability to run natively on M1 processors, MacVector 18.1.1 is essentially identical to MacVector 18.0.1 with the exception that the embedded Python framework has been updated to version 3.9.
Cosmetic Changes for Big Sur
The main application icon and window toolbar appearance have been updated to match the macOS Big Sur “look and feel”.
Improved Align to Reference SNP Reporting
The align to reference algorithm has been slightly tweaked to do a better job of aligning reads that have insertions relative to the reference. The SNPs tab has been revised to use standard reporting for both nucleic acid SNPs and for corresponding changes to amino acid sequences in CDS features. In addition, small deletions are now reported, again using standard nomenclature.
Misc
The use of a comma as the decimal point separator is now supported throughout MacVector for international localization.
Import of GFF files has been improved.
MacVector 18.1 is fully supported on macOS Sierra to macOS Big Sur.
MacVector 18
Released Dec 2020
Overview
MacVector 18 adds a number of new functions, including the ability to read several requested file formats such as Sequencher assembly project files along with Serial Cloner and SnapGene sequence files. There is a new CRISPR PAM sequence searching function and a Trim by Quality option for Sanger sequence files. Finally, there are major enhancements to the protein multiple sequence alignment visualization of domains and the usual macOS compatibility enhancements.
MacVector 18.0 is fully supported on El Capitan to macOS Big Sur. Plus MacVector 18.1 will be released very soon with full Apple Silicon Universal Binary support (ARM64 and X86_64).
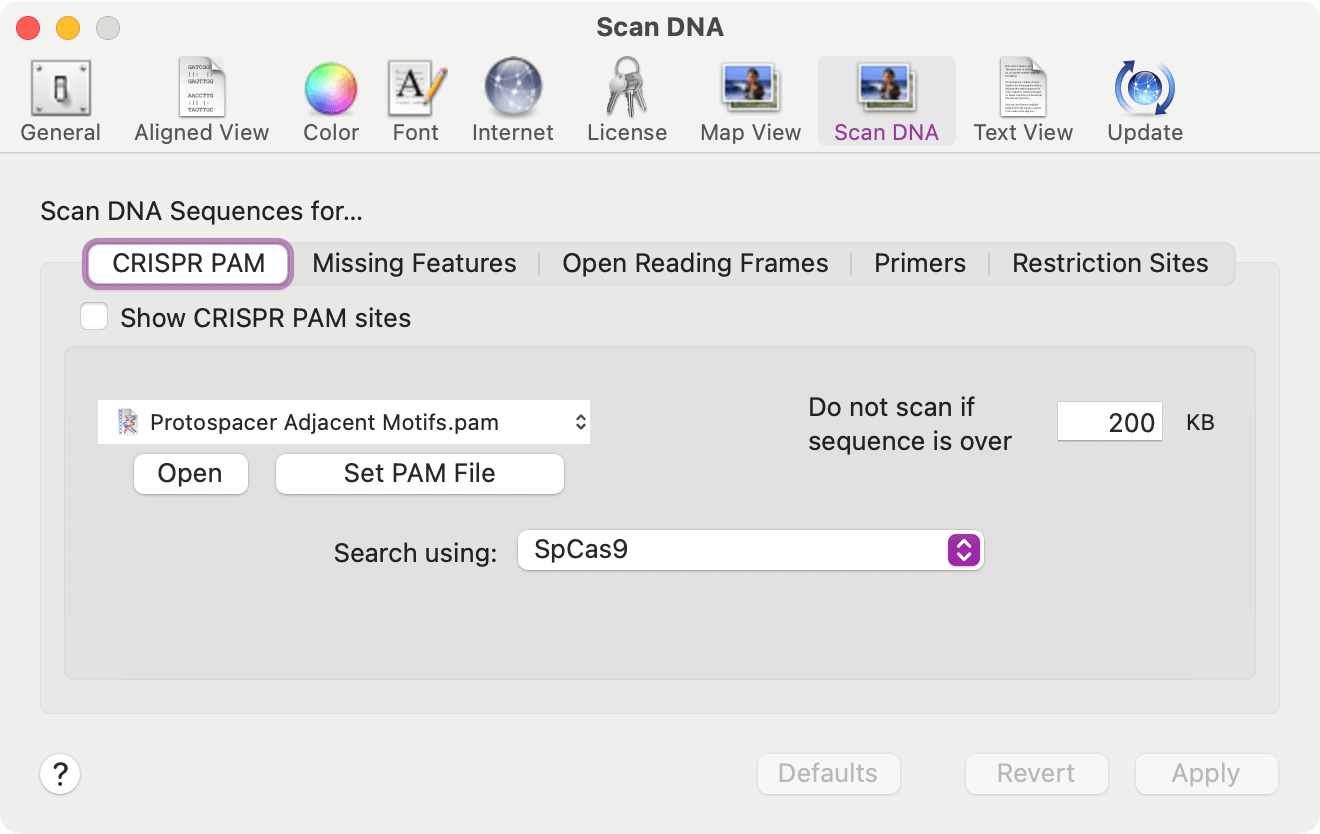
Searching for CRISPR PAM Sites
A new tool Analyze | SCAN DNA FOR… – CRISPR PAM sites… menu item will scan Nucleic Acid sequences for Protospacer Adjacent Motifs associated with the CRISPR Cas9 and related enzymes cleavage and modification functions.
Support for Additional File Formats
MacVector 18 wil import:
- SnapGene .dna files
- xdna files from Serial Cloner
- Sequencher projects
Enhancements to Outlining Shared Domains in Aligned Sequences
There is a new Features tab in the protein multiple sequence alignment window where you can view, edit, create and/or delete features in each of the aligned sequences.
Trim by Quality
Both the Align to Reference and Assembly Project windows now let you trim reads based on quality.
Miscellaneous Enhancements
There have been a large number of minor enhancements to smooth out workflows and improve compatibility with the macOS and other applications. In particular, MacVector 18 now includes embedded versions of Python and Perl as recommended by Apple.
MacVector 17.5
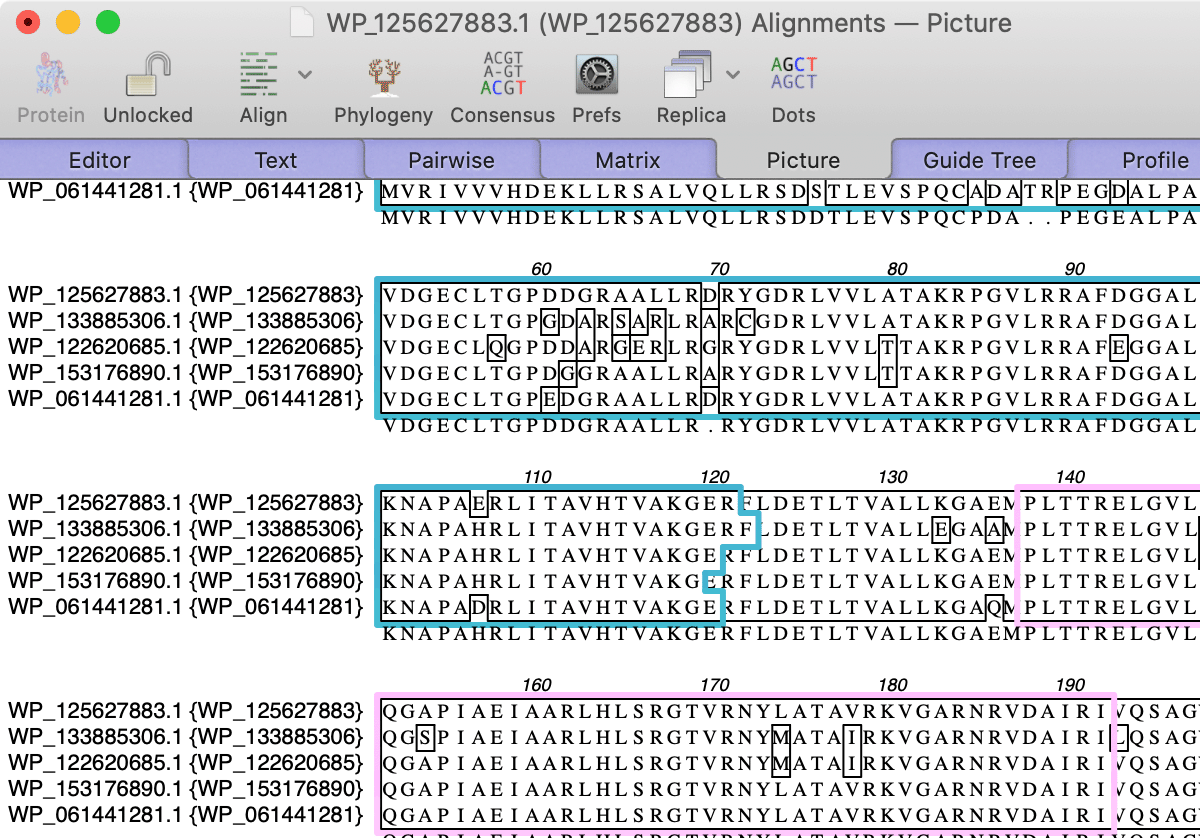
Outlining Shared Domains in Aligned Sequences
Multiple sequence alignments now retain feature information and can use this to outline shared domains in the Picture output tab.

de novo Assembly of PacBio and Oxford Nanopore reads with Flye
Flye is an assembler algorithm tuned to assemble poor quality long reads such as those produced by PacBio and Oxford Nanopore sequencers.
Contig and Align to Reference Editor Enhancements
There have been a number of enhancements to these editors.
Residue Background Colored by Quality
There have been several changes to provide improved support for quality values of de novo contigs and reference assemblies.
A Shading toolbar button lets you turn on coloring based on quality and edited residues are visualized with a blue background.
Base Calling with Phred

You can now directly run phred on Sanger sequencing trace files in the Align to Reference Editor by clicking on the Basecall toolbar item with the appropriate sequences selected;
Editing Enhancements
There are some new context-sensitive menu items in the Align to Reference Editor tab to Delete Clipped Residues and Close Gaps by Deleting Residues. You can also Nudge reads in an alignment
Miscellaneous Enhancements
There have been a large number of minor enhancements. Some, such as reworking code behind the scenes to replace deprecated Apple functions and refactoring code for better stability and performance help ensure that MacVector will continue to work on upcoming releases of macOS and take advantage of improved hardware. There have also been improvements to Dark Mode support in many area and much better handling of the labels in crowded Map views.
MacVector 17
Released February 2019
Dark Mode
MacVector 17 supports macOS Mojave’s Dark Mode.

Scan For… Missing Primers
Automatically scans for and displays primer binding sites from your own Primer Database.

Restriction Enzyme Picker
A new compact interactive interface for selecting and filtering Restriction Enzymes to simplify the identification of useful enzyme cut sites in your sequences.
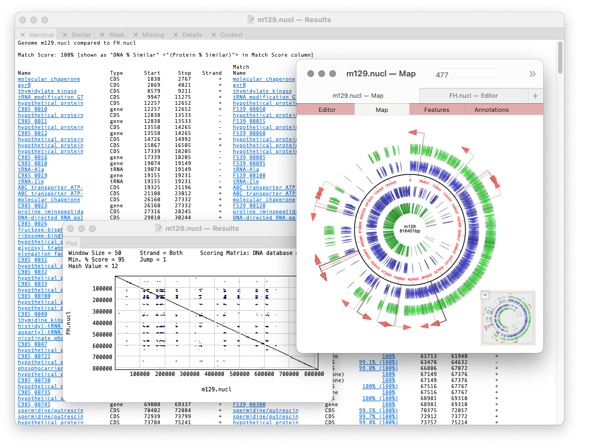
Compare Genomes
Compares two related annotated genomes (or smaller sequences) to identify and list, in spreadsheet form, identical, similar and weakly similar features along with missing features.
Gibson/Ligase-Independent Assemblies
Automatic primer design and assembly of constructs for Gibson Assembly or Ligase Independent Cloning methods, complete with the effects on CDS translations.

How Do I?
A new easy to access menu lists videos and simple tutorials to common workflows. Every tool dialog also has direct access to a simple video/tutorial on how to use it.
Assembly Problems tab
Identify mis-assembled genomic sequences based on excessive mismatches, discontinuous reads and other common problems.
Coverage Tab
Compare different sequencing datasets assembled against the same reference sequence with expression level comparison.

Redesigned Assembly Project
Each assembly job creates its own folder for easier organization of multiple datasets, multiple reference sequences and repeated jobs.
Use of APIKeys with Entrez and BLAST
The NCBI have introduced a new system for accessing the Entrez database over the internet. MacVector now supports those APIKeys
Miscellaneous Changes
- You can now copy and paste features between sequence documents.
- You can now select a short sequence in a Read in the Align To Reference Editor tab, right-click to bring up a context sensitive menu, and then select all of the other aligned reads that contain that a sequence.
- Some of the nomenclature and interactions in the Primer3 dialog box have been cleaned up to simplify its use.
- You can now add sequences to the Align To Reference window from multi-sequence GenBank files.
- GenBank multi-sequence files now open by default as individual sequences.
- When results are generated for the Bowtie Coverage tab, the name of each feature is now displayed exactly as per the label used in the Map tab allowing you more control over exactly how the text appears.
- There is now an option in the Database | Auto-annotate Sequence… interface to automatically “fix” CDS features. This will change the stop location if the match creates a longer or shorter open reading frame and will also change the contents of any /translation= qualifier to reflect the new translated coding sequence.
- The Align to Reference algorithm is now multi-threaded.
MacVector 16.0
Released November 2017
Scan for.. Missing Features.
Sequences are automatically scanned against a Common Features library and missing features are displayed. A simple right-click converts them to a permanent feature.

Batch Translation using Applescript
Produce individual protein sequence files, or FASTA files with all translated CDS regions from a folder of DNA/mRNA/cDNA sequences.
SPAdes: de novo assembly
This new algorithm offers support for mixed assemblies (e.g. Illumina, PacBio and Oxford Nanopore in the same assembly), has a smaller RAM footprint than Velvet and typically produces longer contigs.
Unified Feature Editor.
A new editor that combines the GenBank data and Symbol appearance into a single dialog for simpler editing.
Closing bacterial genomes
A new tool helps circularize bacterial genome assemblies by resolving ends where there are overlaps.
MacVector 15.5
Released May 2017

Graphical BLAST Results
A new BLAST results tab displays a graphical alignment of the query sequence aligned against each high scoring segment pair of the BLAST hits. This allows you to clearly see which genes or features your query is aligning to. For each hit, you can choose to download the entire sequence, or just the aligned segment plus ~2kb either side.
Automatic ORF Display
MacVector now automatically searches for open reading frames in every DNA sequence that you open. You can quickly annotate the ORF to your sequence with a right mouse click.
Align to Reference: new tools
Many new tools have been added for simplifying the use of MacVector for closing the gaps in bacterial genome sequencing projects.
- Export Consensus with/without Gaps
- Align Selected Reads
- Delete Selected Reads
- Reset (unalign) Selected Reads
- Export Selected Reads as FASTA/FASTQ
- Select Matching Pairs
- Extend Reference with Selected Read
MacVector 15.1
Released November 2016
BLAST and Entrez
A complete rewrite of BLAST and Entrez to make them compatible with the new NCBI infrastructure. As of November 2016 only MacVector 15.1 and later will connect to the BLAST and ENtrez databases.
Misc.
Many bug fixes.
MacVector 15.0
InterProScan
Scan proteins for functional domains against a variety of sequence, protein family, domain and motifs databases (inc. UniProt, PROSITE, HAMAP, Pfam, PRINTS). Annotate domains to your sequence with a link to the database.
Translated Multiple Sequence Alignments
Align DNA sequences based on their amino acid translations. Display DNA sequences and their translations at the same time. Align the protein sequences using ClustalW, Muscle or T-Coffee to see the effect on the underlying DNA sequences.
Align proteins against a reference
You can use a protein sequence as a reference so that the display keys off that sequence when showing similarities.
Applescript and Auto Annotate
Auto-annotation has joined the growing number of MacVector tools that support Applescript. Batch annotate folders of blank sequences.
CRISPR Indel Analysis.
A new setting in the Align To Reference interface tunes the algorithm to more cleanly identify and display the short insertions and deletions that are frequently seen following CRISPR editing of a target.
MacVector 14.5
Agarose Gel Simulation MacVector 14.5 introduces a photo-realistic agarose gel simulation with recreations of restriction digests of linear and circular molecules under a variety of electrophoresis condition.

Align To Folder now handles paired read files.
Reduced Memory Footprint: for all editors but especially for Align To Reference alignments against large fastq files.
Edit | Remove Gaps function to remove gaps in single sequences and also in the Align To Reference and Contig editors.
Documenting cloning procedures Fragments on the Cloning Clipboard can now be copied as a graphical PDF object – great for creating drawings in e.g. Adobe Illustrator outlining the derivation of a construct.
Version 14
64-bit Architecture: MacVector 14 is a fully 64-bit application. The main utility of this is that MacVector can take full advantage of all of the memory installed on your computer, allowing it to handle larger sequences and alignments.
Primer Database Support MacVector now directly supports the concept of a “Primer Database”. All primer design tools can use or save directly from the primer database.
Primer Database Search: scan sequences against the primer database.
Installation and Use Without Administrative Access MacVector that can be completely installed, licensed and used without requiring Administrative access to the machine.
Restriction Enzyme Methylation Sites All of the enzyme files have been updated to include methylation information.
Assembler Bowtie Improvements Bowtie has been updated to version 2 which can handle gaps in the aligned reads or in the reference sequence.
Primer Design – Test” mode now has a text output similar to the old Test PCR Primer Pair functionality, with details of all of the possible products generated by the pair of primers.
Version 13.5
Align To Reference now handles alignments around a circular sequence and will export mapped reads in fastq or fast format.
Align To Folder can now perform alignments against fasta and fastq files and outputs matching reads in fasta or fastq format.
Pustell Matrix (“Dot Plot”) Enhancements: The performance of large (i.e. genome-sized) Pustell Matrix dot plot alignments has been dramatically improved.
Assembly Coverage report: Reference alignments now have a separate coverage report tab that lists the read coverage for every gene and CDS feature in the reference sequence.
You can now export unassembled reads from Bowtie and Velvet alignments as fasta or fastq files. This lets you filter out reads that match specific sequences so you can focus subsequent alignments using a subset of reads.
You can now reset the circular origin of circular sequences to any arbitrary position. Simply click between the residues where you want the new origin to be, then right-click (or -click) and choose Set Circular Origin from the popup menu.
Version 13
Quicktest Primer and Restriction Enzymes displays restriction enzyme sites around the primary binding site of the primer. Sites that are created or destroyed by mismatches in the primer or due to the addition of a tail, are shown on the sequence along with ‘One out’ sites which are color coded to indicate whether they are silent mutations or not.

Testing Primers When you enter a pair of primers into Design Primers (Primer3) the interface switches to a new testing mode, TEST PRIMER PAIRS. At this point all parameters are relaxed so that your primers are always accepted.
De Novo NGS Assembly Velvet has been added to Assembler for de novo assembly of short reads. Velvet is ideal for assembling Illumina sequencing reads of bacterial genomes on a mid range Mac. With paired read data it produces very good contigs.
Tabbed Results windows The results from every analysis of a sequence are tabbed to stop window clutter.
Applescript Applescript functions now allow control of file opening and saving. For example you will be able to script MacVector to batch open and save in a new format. Sample scripts are included.
Chromatogram enhancement A new tab in the Chromatogram sequence window displays the quality values and areas under each trace curve for each sequence residue in a tab delimited format that can be copied into Excel for additional analysis.
Version 12.7
MacVector Free
This is the first release with a free basic edition. Users can use MacVector Free to open or download sequences in any supported format, edit them, print, copy sequences, text and graphics, and save in any supported format. Users are able to perform simple click cloning operations, generate new constructs and have full control over the appearance of features. Entrez and BLAST are still available along with the Find functionality.
Cloning Clipboard simplifies the creation of new DNA constructs. The new functionality lets you join molecules together using an intuitive drag and drop interface. The history of every ligation event is recorded with the sequence showing the enzymes used, the date and any end modifications.


Dot Plot Performance Enhancements allowing you to now run pairwise alignments of whole genomes in just a few minutes.
Align To Reference Performance Enhancements
optimized to be of more use for aligning large numbers of Next Generation Sequencing reads against large genomes.
Optimized Reverse Translations allowing you to optimize codon usage when reverse translating a protein.
Version 12.6
Primer Enhancements
A new QuickTest function allows easy design and analysis of primer sequences. You can view secondary structure in real time as you enter a primer sequence and add restriction sites or mismatches for site directed mutagenesis whilst viewing the modified translated sequence.
Import annotation from Genome Browsers Support of GFF, GFF3, and BED files to annotate blank sequences. Allows you to easily import annotation from Genome Browsers. Create new sequence(s) with complete annotations by copy and paste of GenBank, EMBL and FastA documents.
Assembler improvements Major performance enhancements for displaying large assemblies.
Import existing Assemblies Import BAM/SAM alignments for displaying.
Performance enhancements Dot Plots (Pustell Matrix) can now handle small genome vs genome comparisons. For example a pair of E.coli genomes can be aligned in five minutes on an 2007 MacBook Pro. Major performance enhancements to Map Graphics for easier viewing of annotation rich genome sequences.
Version 12.5
Improved NGS support: supports Bowtie assemblies of Fastq datasets. Collections of contigs can be exported in FastQ format for additional analysis. SNP detection and reporting has been enhanced with VCF output from Bowtie alignments and listing of all the codon and amino acid changes between the consensus and reference sequence alignments.
Muscle and T-coffee have been added to the Multiple Sequence Alignment analysis interface, complementing the existing ClustalW algorithm.
Miscellaneous Changes
A number of older editors and lists (Restriction Enzymes, Subsequences, Scoring Matrices) have been rewritten in Cocoa, providing a cleaner interface and more selection and cut/copy/paste options.
Performance has been increased in many areas.
Version 12.0
Licensing: introduction of Personal licenses and Network Roaming Licenses.
Circular Sequence Support: Selecting across circular origins
Map View Enhancements: Double-stranded sequence display. Show CDS features as translations when at residue level, Show 3/6 frame translations of the sequence, Show Primer features as residues at residue level.
Map View Navigation: Use arrow keys to nudge/slide through a selected segment (and have any results update appropriately), Navigable overview panel
Virtual Cloning: Show unique enzymes in unique color/font with compatible enzymes for left/right ends of a digested fragment highlighted in red/green. Show staggered RE cut sites in Map view when zoomed to residue. Show one out sites show in greyed out color with an asterisk next to name (e.g. EcoRI*).
Sequence Editor View: Allow users to change the case and color of the text in the editor, driven by the map view feature settings.
File Import: New From Clipboard option allows easy import of GenBank and EMBL formats
Sequence Annotation: Drag and Drop (or right click) to add results to a sequence as a feature
Version 11.1
Workflow Enhancements: This release has a large number of changes designed to simplify and speed up many common workflows and to provide better integration
with the Macintosh operating system.
Multiple levels of Undo for the Multiple Sequence Alignment, Contig/Align to Reference and
Trace editor windows
Version 11.0
Auto annotation function that will scan a folder full of existing annotated sequences and automatically add matching features to your bare sequence.
Click Cloning has also become both easier to use and more powerful with the ability to manipulate overhanging ends and a new digest/ligate dialog. In addition, you can now display 3 or 6
frame translations directly below the sequence in the editor.
Assembler module has also been enhanced to provide support for next generation sequencing machines. Short read data may be imported in Fastq format and as long as you have a powerful enough Mac, de novo assemblies can be created.
Floating toolbar containing buttons for all common MacVector analysis functions. You can customize the toolbar to show just the functions you use most often or show
them all for rapid access to every available algorithm. You can even add any of the buttons to sequence window toolbars for quick access to your favorite
analysis algorithms.
Version 10.6
VNTI Database Support: Addition of Vector NTI database Browser MacVector, Inc. has just released MacVector 10.6. This release sees the introduction of a Vector NTI database import
function that allows MacVector to directly read sequence data from databases created by Vector NTI Advance v10 or earlier, even if the database resides on a Windows machine accessible over a network.MacVector 10.6 reads all of the standard features and annotations associated with each sequence. Also, since MacVector follows the Genbank format for the features table and is always kept up to date with the latest Genbank release, it has the added benefit of migrating any old and deprecated feature information contained in the Vector NTI file into the current nomenclature.
Version 10.5
Align To Reference. The Sequence Confirmation tool was renamed and now supports alignment of cDNAs to genomic sequences to aid in the identification of splice sites and introns.
Version 10.0
Licensing: introduction of standard licensing to replace USB dongles
Dynamic Restriction Enzyme Analysis has had an interface overhaul with dynamic automatic restriction enzyme searching and display to simplify clone construction.
Feature editor to simplify the creation of GenBank style annotations has been added along with a redesign of the Entrez browser with support for more databases and retrieval of genomic contig sequences.
Primer design has also been updated with a new Primer3-based primer design function with support for real-time PCR primers.

