Tag: weeklytip
-
MacVectorTip: How to Control the Length of Window Title
If you are having difficulties viewing the name of your sequence in the title bar of a window, it may be because you have “Full Titles” turned on. So if your window title looks like this; Then open MacVector’s Windows menu and deselect Show Full Titles. …and you now just see the name of the…
-

MacVectorTip: Assembling Nanopore or PacBio Long-Read Data with Flye
In the previous post we discussed the various ways in which you can analyze Oxford Nanopore’s long read data. For de novo assembly we recommend using Flye, which can also be used with PacBio data. Here are some tips to get the most out of Flye. IMPORTANT: MacVector simply wrappers around the Flye executable algorithm which depends on…
-
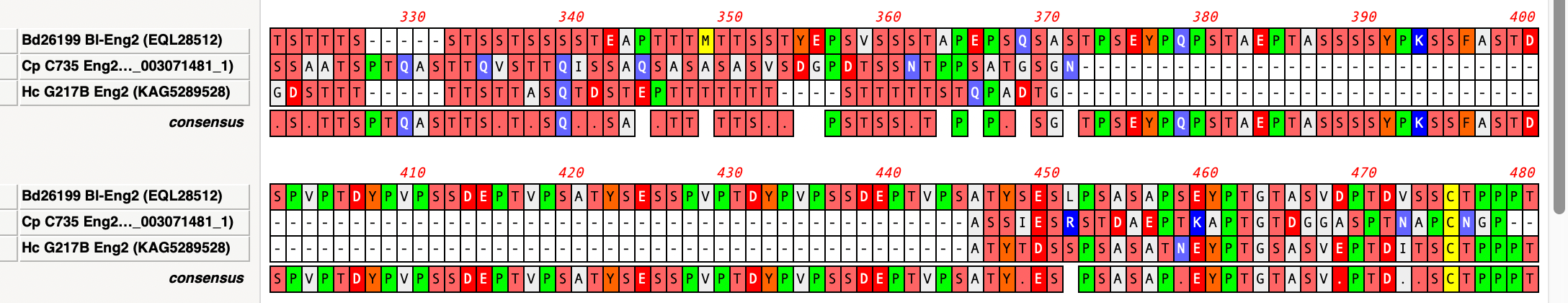
Handling Gaps in Multiple Sequence Alignment Consensus Calculations
By default, MacVector ignores gaps when calculating the consensus of a multiple sequence alignment. However, this can lead to some unexpected results. For example, consider this three sequence alignment where one sequence has a long insertion compared to the other two. In this case it does not seem reasonable to believe that the “consensus” should…
-
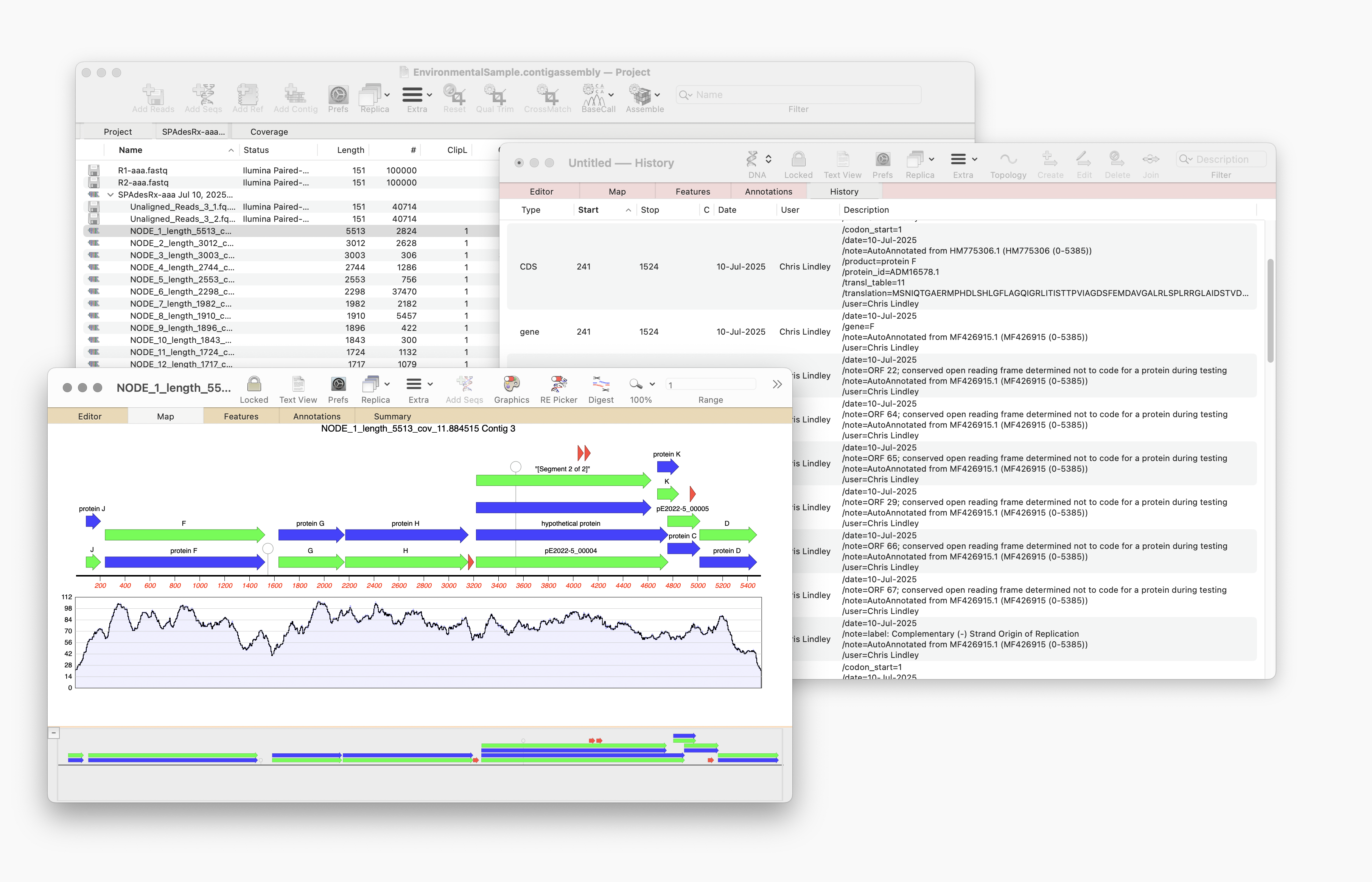
Automating annotation of sequences via BLAST
MacVector 18.8 is out and it’s packed with new tools! MacVector 18.8 has tools to help you identify and annotate unknown, unannotated or partially annotated sequences. Ideal for identifying contigs from a de novo assembly. One of these new tools is AutoAnnotate (via BLAST) Auto-Annotate (via BLAST) is similar to Auto-Annotate (local), except instead of using curated sequences on your own…
-
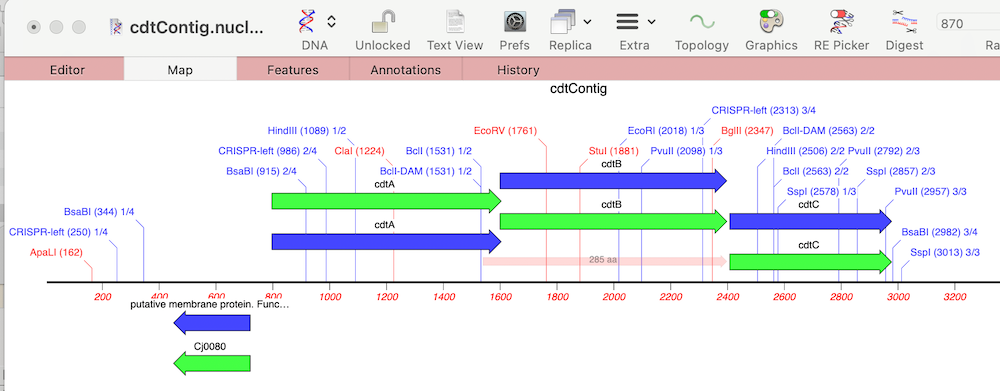
MacVectorTip: Annotating and Comparing Genome Segments
In last week’s tip we showed you how to filter NGS read data to pull out and assemble just those reads that represent a specific gene of interest. Now let’s see how to annotate the single contig we generated and compare that to a reference genome. First, from the Contig Editor, you can save the consensus in MacVector…
-
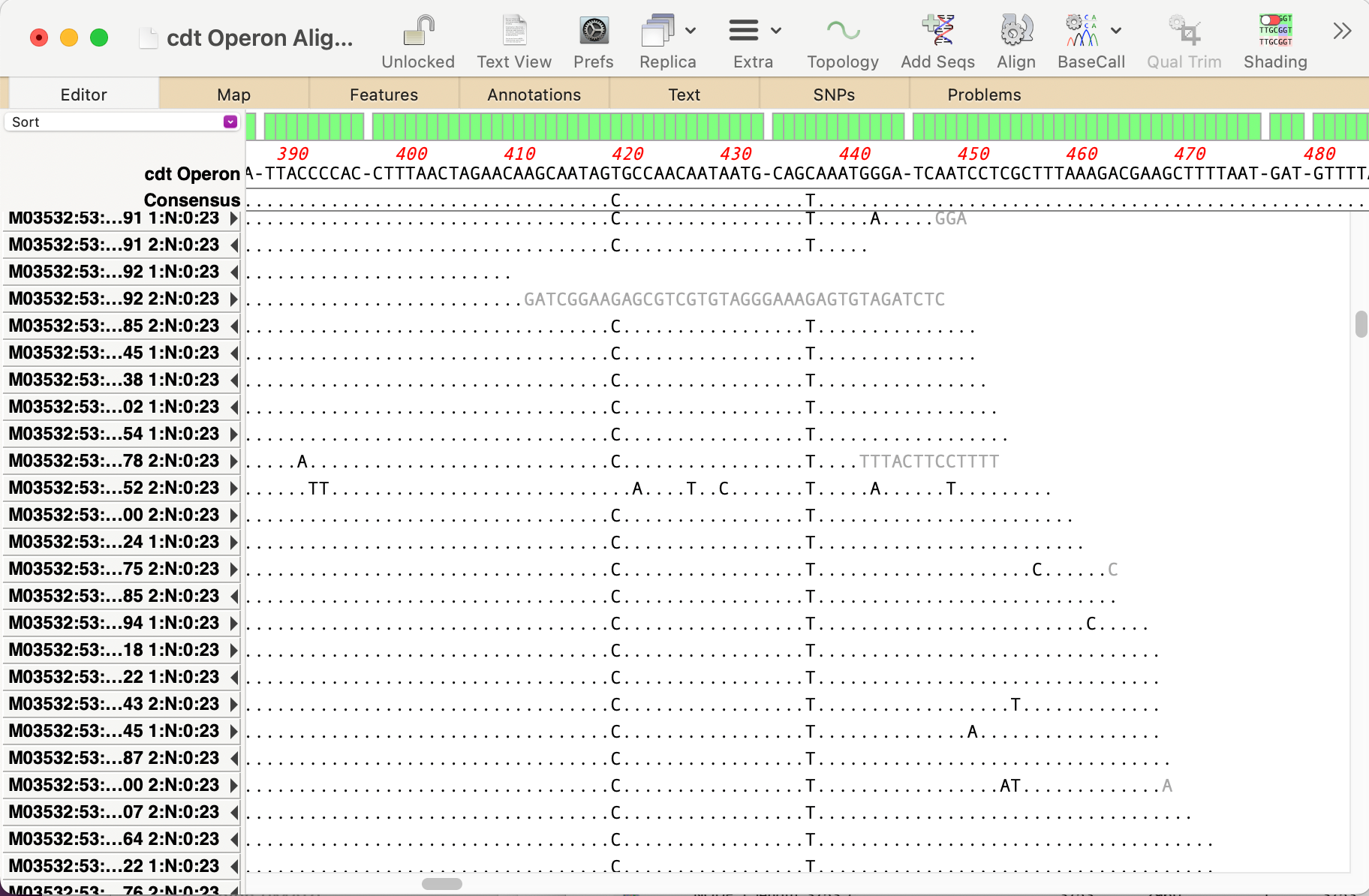
MacVectorTip: Use Align to Folder to filter NGS data for specific genes
Even the latest Macintosh computers loaded with as much RAM as you can afford will still struggle to de novo assemble genomes much over 50 Mbp. But, often that is not required. If you are just interested in a few genes, or a specific region of a chromosome, you can use Align to Folder to filter the…
-
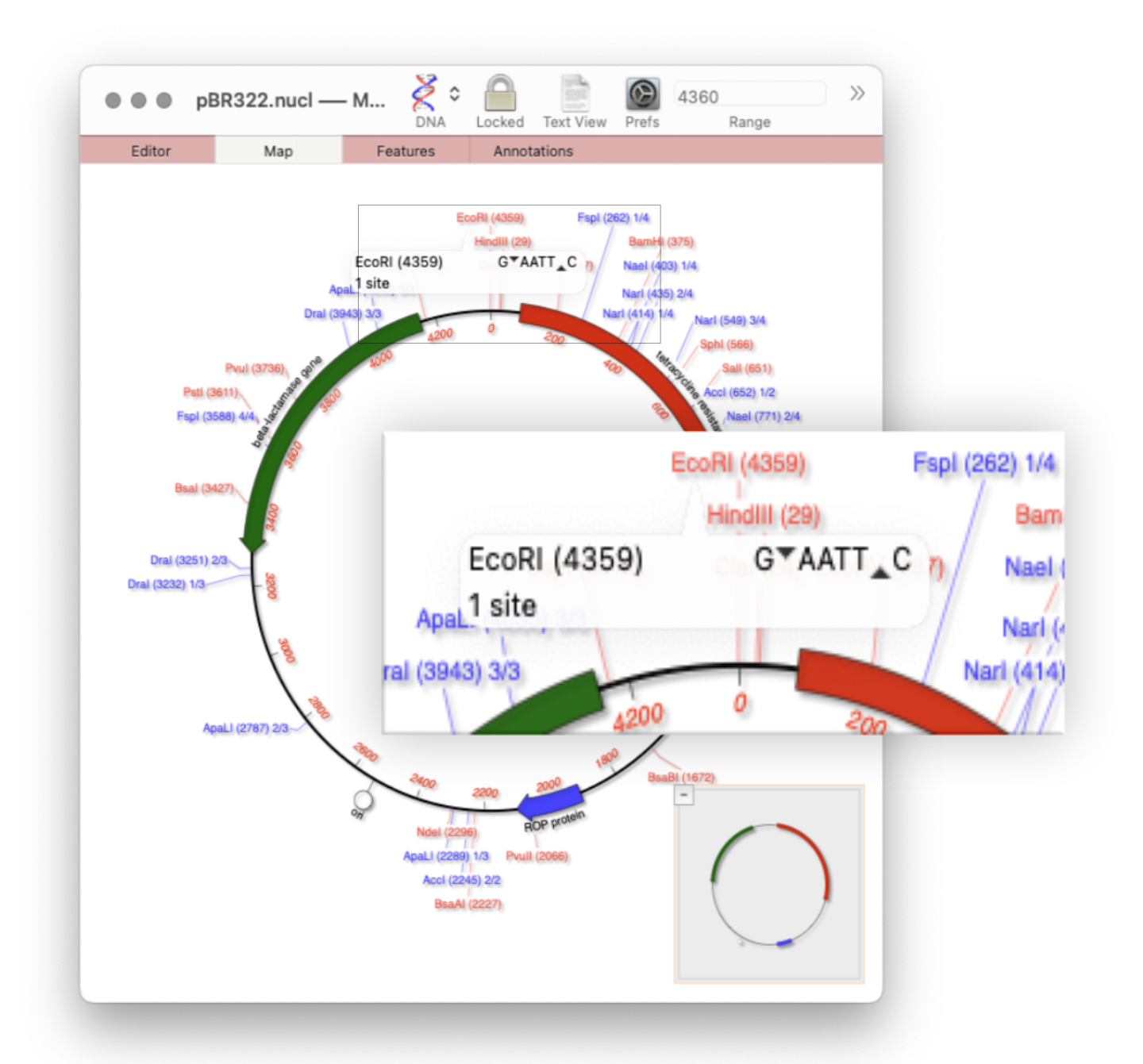
MacVectorTip: Restriction enzyme sites and tooltips
Quickly viewing the recognition sequence and cut site of a restriction site is very easy in the Map tab. By default MacVector’s Scan DNA For… tool will automatically display restriction enzyme recognition sites in the Map tab. If you hover your mouse over a restriction site, a tooltip will show you the restriction enzyme recognition site, the location of the cut…
-
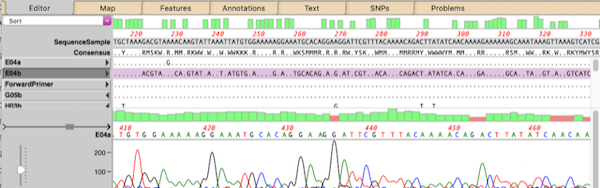
MacVectorTip: Advanced Align to Reference Editing
You can use the Analyze | Align to Reference function to align other sequences (Sanger chromatograms, plain sequences or even NGS data collections) against a reference. Once aligned, the Editor lets you perform all the usual editing functions using an “overwrite” mode – select the residue you want and type the new residue to replace…
-

MacVectorTip: How to Toggle Between Single-Letter and Three-Letter Amino Acid Translation Code
Many views in MacVector display amino acid translations above or below DNA sequences. Typically, these are from CDS features, but can also be the 3/6 frame translation of a sequence. You can display the amino acids as either the single-letter code, or as the three-letter code. You can toggle the setting using the MacVector | Preferences ->…
-
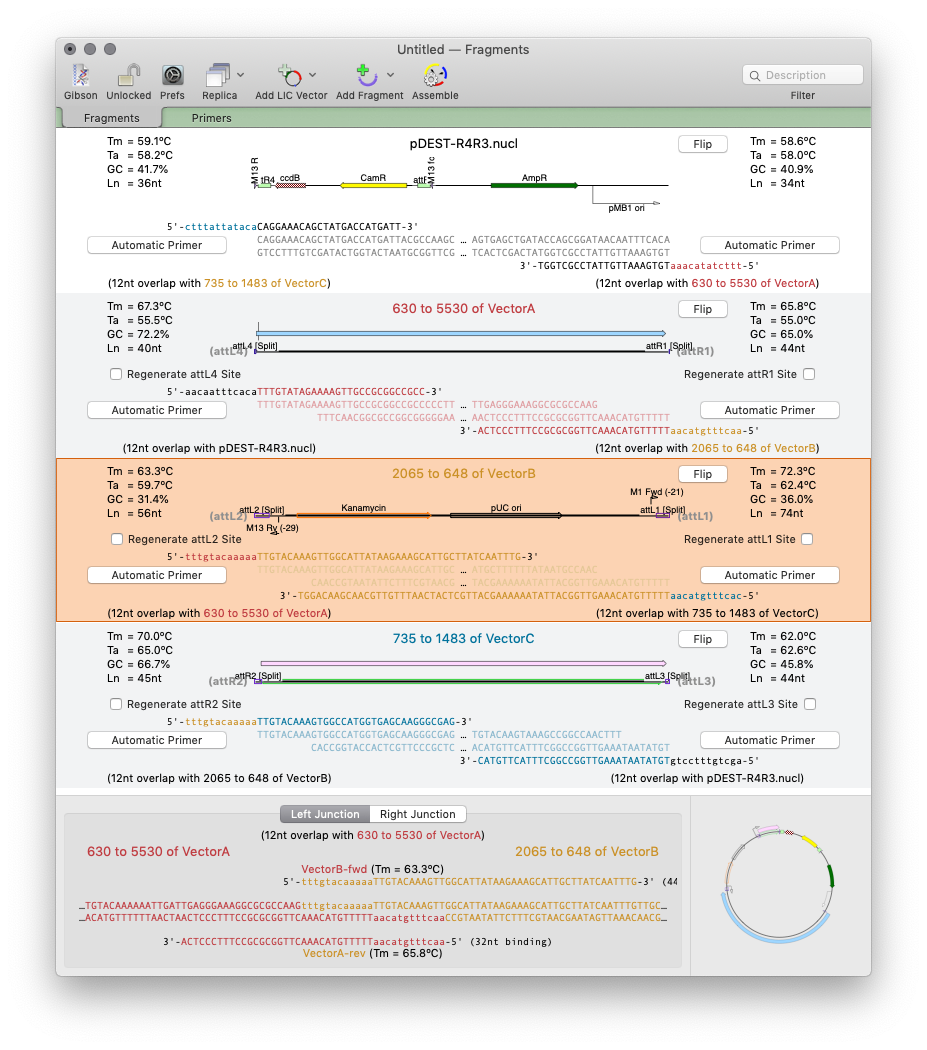
MacVectorTip: Drag and drop in the Gibson Assembly window
Over the years, we have added a lot of drag and drop functionality to MacVector. Of course, as with any application, it is not always obvious that you can drag and drop to accomplish tasks because you literally have to drag and drop to discover you can do it at all! So here is the first of…
