You can use Assembler to align millions of short Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) reads against genomic reference sequences. This is useful for identifying SNPs and other variants in clones or mixtures of isolates compared to a known parent or reference, or for the first step in a scaffolding-based assembly of a related species. There are blog posts describing this functionality here and here.
Adding Reference and Reads to a Project
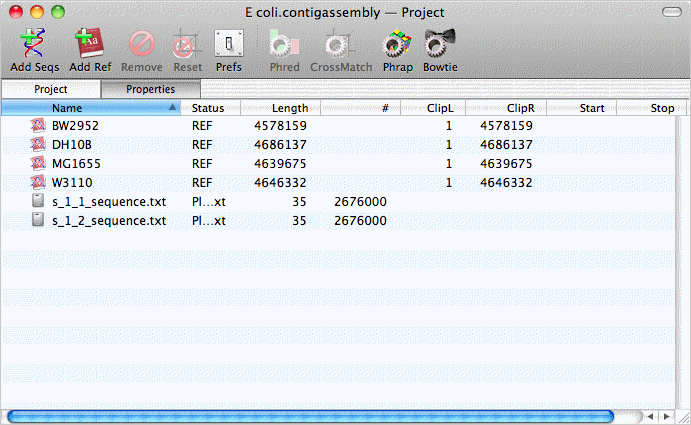
Assembly projects have two toolbar buttons for adding sequence data to the project. The Add Seqs button is used to add read data to the project – these are typically FastQ formatted files containing sequence data from Illumina Solexa, SOLiD or 454 sequencing runs. To save disk space, the files are not copied – MacVector just notes their location, so its important not to move them after you have created a project. The Add Ref button lets you add one or more reference sequences to the project – these can be in any format recognized by MacVector. The image below shows a project populated with 4 Escherichia coli reference genomes and two FastQ read files representing paired-end reads from an E. coli clone.
Assembling Using Bowtie
Bowtie can assemble reads against more than one reference sequence in a single run, so we can just select all the reference sequences and the two sequence files, then click on the Bowtie button;
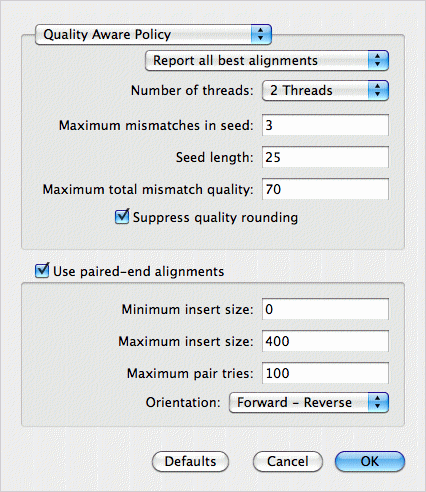
MacVector detects the fact there are two read files, so enables the Use paired-end alignment checkbox. The Report all best alignments option ensures that each read in the sequence files can align separately to each of the four reference sequences. After clicking OK, the job runs, taking about an hour on a laptop for this data (four 4.6 Mb genomes aligned against ~5 million reads).
Viewing Reference Contigs
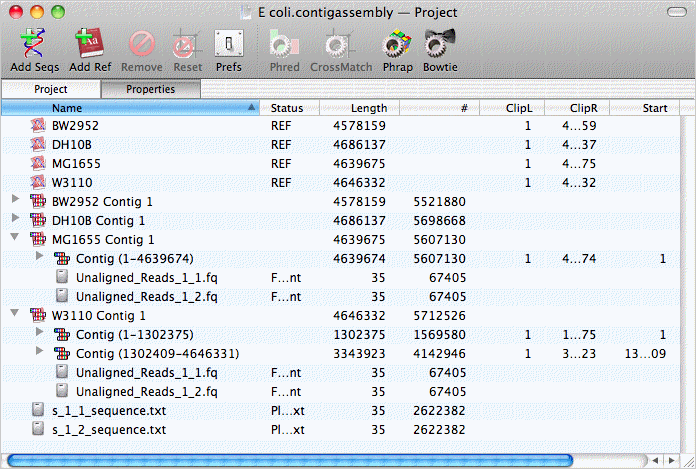
When completed, a reference contig assembly object for each reference sequence appears in the project window. Each of those can be opened to reveal the child contigs enclosed by them. For a full length alignment, there is just one, but W3110 has two contigs with a short gap between them;
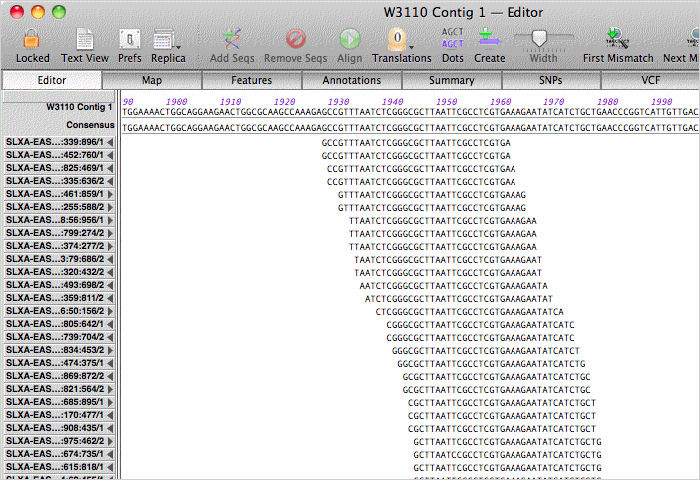
Double-clicking on a contig opens up the contig editor/viewer. You can scroll through the actual aligned assembly;
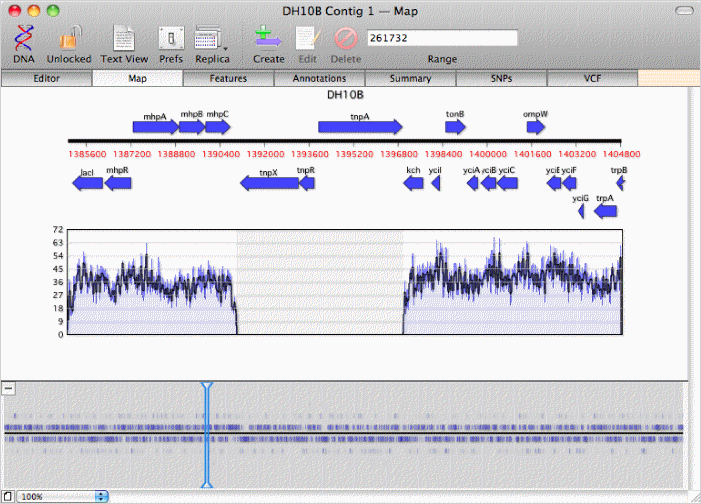
zoom in on regions where the coverage map indicates there are no overlapping reads, like this transposon inserted in DH10B;
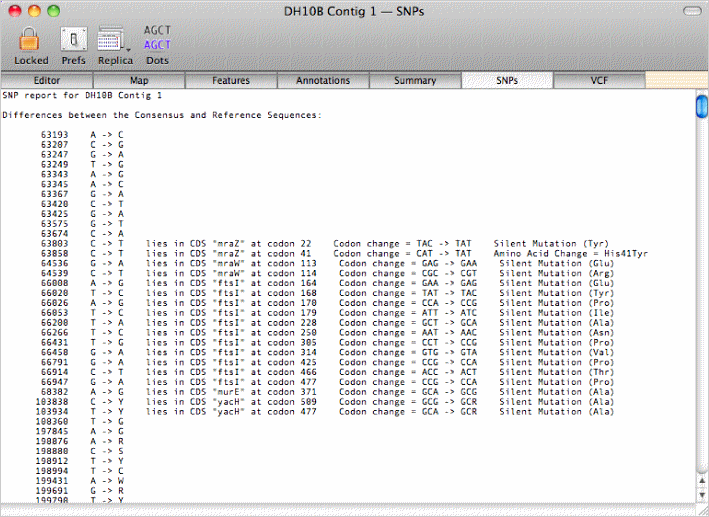
or view a summary of the SNPs in the consensus sequence from the reads and the affect these would have on the amino acid sequence of any annotated CDS features;