Here’s the basic steps of bringing sequences into MacVector.
Starting Point Dialog
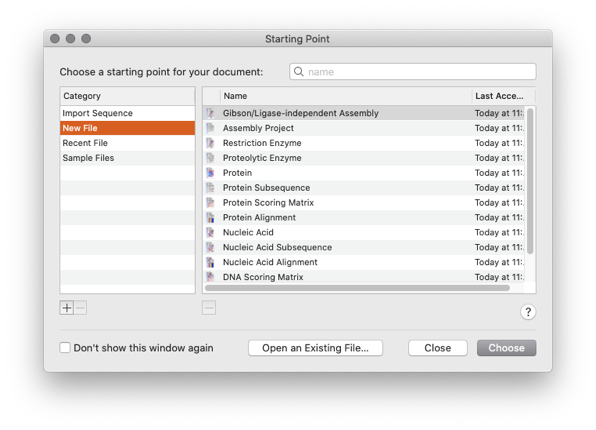
When you start MacVector for the first time you will be presented with the Starting Point Dialog. This allows you to create a New MacVector file, to open a recently opened file or to Open an existing file
You can also create a Gibson Assembly project, an Agarose Gel, an Assembly Project or Align sequences to a reference.
Double clicking on a file or dragging it to the Dock
Usually this will just work. However, this is always reliant upon the operating system deciding which application to use to open a file. If you have multiple sequence analysis applications installed, or your file has no file extension you may find that the file opens in the wrong application. If you right click and choose OPEN WITH you can choose which application to use.
Using the FILE > OPEN menu
This is the traditional, always works, option. You do not have to worry about file extensions as well. MacVector will look inside the file and try to “automagically” use the most appropriate file format importer.
Entrez Browser
MacVector has an Entrez browser that lets you search the online Entrez GenBank database using keywords and retrieve matching sequences either directly to disk or to open directly in MacVector. You can access this via the Database | Online Keyword Search for Sequences (Entrez) menu item.
New From Clipboard
If you have copied any sequence data to the clipboard then you can directly open this using the New From Clipboard function. This also recognises Genbank formats if you have copied a file directly. For example many websites allow you to download a sequence by displaying a Genbank sequence. You can easily copy such sequences and directly paste into MacVector.
Import Features from a Genome Browser.
If you have a blank sequence and no existing curated sequences you can use Import Features from GFF/GFT and BED files to bring features in from one of many Genome Browsers that allow you to export date in a BED/GFT or GFF file. This function allows you to annotate an unannotated or partially annotated sequence with annotations (or features) contained within a BED/GFF/GTF/GFF3 file. Don’t forget the Auto Annotation. tool scanning your sequences against your own annotated ones either.